The OV-3 details the operational information exchanges between nodes, as defined in the OV-2, Operational Node Relationship Diagram.
Information exchanges help define the interoperability requirements associated with the operational capability of interest. Although the primary purpose of this view is to specify information exchanges, an OV-3 may also list flows of materiel, energy and human resources.
Usage
The intended usage of the OV-3 includes:
- Definition of interoperability requirements.
Product Description
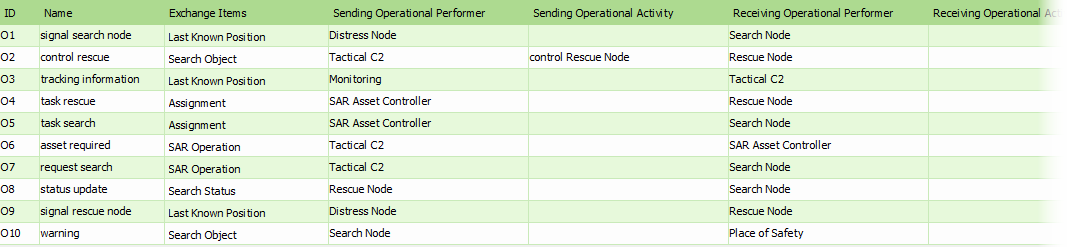
The OV-3, Operational Information Exchange Matrix, identifies the information transfers that are necessary to enable the nodes to achieve a business objective. This view is initially constructed from the information contained in OV-2, Operational Node Relationship Description, and OV-5, Operational Activity Model; however, OV-3 provides a more detailed definition of the information flows between nodes.
The Operational Information Exchange Matrix details information exchanges by identifying which nodes exchange what information, with whom, why the information is necessary, and the key attributes of the associated information products. Information exchanges express the relationship across the three main M3 elements for the Operational Viewpoint (operational activities, nodes, and information flows) with a focus on the specific aspects of the information flow and the information content. OV-3 is one of a suite of operational views that address the information content of the operational architecture (the others being OV-2, Operational Node Relationship Diagram, OV-5, Operational Activity Model, and OV-7, Information Model).
The OV-3 maps information elements to the producing and consuming nodes, the needlines between them, and the activities that they support.
An information element is a piece of information that is subject to an operational process. The structure of the information element may be defined by a logical data model (see OV-7, Information Model). Information elements are carried on operation activity information flows (in OV-5) and information exchanges (in OV-2). The same information element may be used in one or more information exchanges.
An architect may specify attributes for the Information exchanges in OV-3. Typical attributes would be “timeliness”, “availability”, “protective marking”, “non-repudiation”, etc.
Multiple information exchanges may be bundled into one needline. In OV-3, this information is captured in tabular form, usually with the needline identifier being shown in one of the columns.
The emphasis in this view is on the logical and operational characteristics of the information being exchanged. It is important to note that OV-3 is not intended to be an exhaustive listing of all the details contained in every information exchange of every node associated with the architecture in question. Rather, this product is intended to capture the most important aspects of selected information exchanges. The table below shows an example of the relevant information content.
| Data Description | Nature of Transaction | Performance Attributes | Information Assurance | Security |
|
|
|
|
|
Creating an Operational Node Relationships (Node-based) table
The OV-3 Operational Node Relationships table identifies the information transfers that are necessary to enable the nodes to achieve a business objective. It details information exchanges by identifying which nodes exchange what information, with whom, why the information is necessary, and the key attributes of the associated information products.
To create an Operational Node Relationships (Node-Based) table:
- Click on Operational Node Relationships (Node-Based) in the Action Artifact area to open the Operational Node Relationships table.
- This opens the Operational Node Relationships table with OperationalExchanges listed. The OperationalExchanges are defined in OV-2.
- For each of the OperationalExchanges:
- Enter its ID
- Select the items involved in operational exchange.
- Optionally fill-in the attributes of operational exchanges.
Creating an Operational Node Relationships (Role-Based) table
The Node Interactions table specifies the information exchanges among nodes. Unlike the node-based table, role-based table focuses on the interactions between roles inside the operational nodes.
To create an Operational Node Relationships (Role-Based) table:
- Click on Operational Node Relationships (Role-Based) in the Action Artifact area to open the Operational Node Relationships table.
- This opens the Operational Node Relationships table with OperationalExchanges listed.
- For each of the OperationalExchanges:
- Create a new OperationalExchange by clicking on the New Operational Exchange above the table.
- This creates a new row of OperationalExchange. Enter its name.
- Select the OperationalConnector that the OperationalExchange realizes. The OperationalConnectors are defined in OV-2.
- Select the items involved in operational exchange.
- Optionally fill-in the attributes of operational exchanges.
MODAF in Visual Paradigm
The MODAF is brought to you by Visual Paradigm, a full-featured development platform. Visual Paradigm provides an easy-to-use, model-driven MODAF tool that supports the development of MODAF views and models. You can create integrated MODAF products and generate architectural documents that facilitate organizations to efficiently coordinate enterprise architecture initiatives.