A database view is the result of a query on the data stored in a database. You can select columns, specify where and join statements to a view and present the data as if the data were coming from one single table. In Visual Paradigm, you can edit database view in a visual editor.
Creating database view
A database view is represented visually with a View shape. You can create a database view from the diagram toolbar or from the entities involved in the database view.
From diagram toolbar
You can create a database view and then edit it by specifying the entities involved. To create a database view:
- Select View from the diagram toolbar.

- Click on the diagram to create a view.
- Enter its name and confirm.

You can now specify the entities involved in the view via the View Editor. To open the View Editor, right click on the background of ERD and select Show Table Record Editor or View Editor from the popup menu. - On the right hand side of the View Editor. Click on the add button. Then, select the entities that are involved in the view and click Apply.
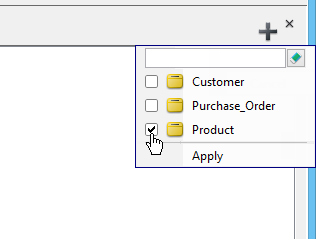
Now, you can specify the view. For details, read the following sections.
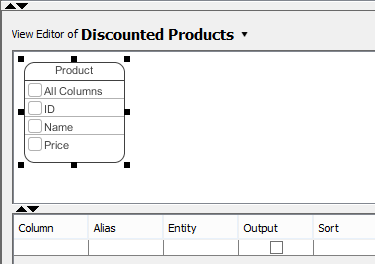
From entities
Instead of creating a blank view and adding entities into the view, you can create a view directly from entities that are involved in the view. To create a database view from entities involved:
- Select the entities in ERD.
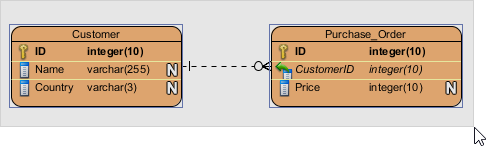
- Click Create View in the View Editor. The View Editor is placed under the ERD. If you do not see it, right click on the background of ERD and select Show Table Record Editor or View Editor from the popup menu.
Now, you can specify the view. For details, read the following sections.
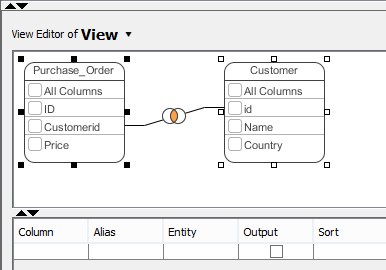
Column selection
A database view contains rows (i.e. the results) and columns, just like a database table. To select columns, simply click on the checkbox of the desired column. Alternatively, select the column in the Column column in the View Editor.
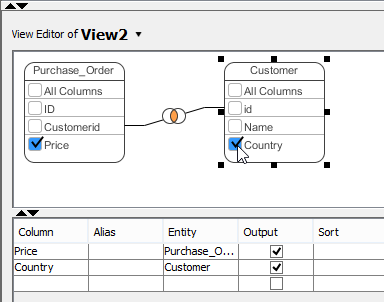
Joining columns
Joining of columns between entities can be done by the resource-centric interface. To do this:
- Click on the source column in the entitiy in View Editor.
- Press on the desired resource and drag it out.
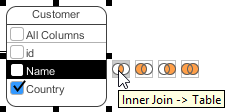
- Drag to the target column and release the mouse button.
Editing database view in View Editor table
There is a table under the visual view editor where you can configure a view’s column alias, sort order, grouping, function, filter, etc.
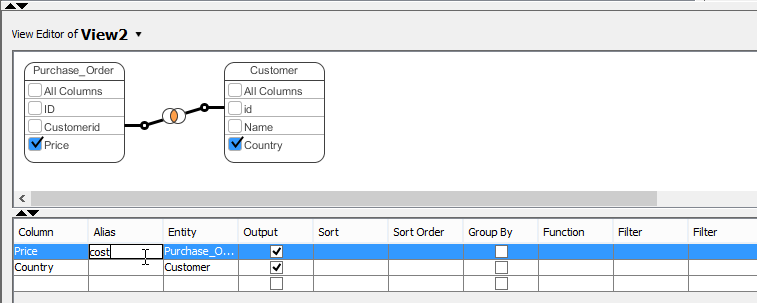
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Column | Correspond to the SELECT clause of a view creation statement. |
| Alias | The displayed name of column. |
| Entity | The entity where the column come from. |
| Output | Check it to include the column into the creation statement of view. |
| Sort | Specify whether to sort the column ascendingly or descendingly |
| Sort Order | Specify the sort column. Records are sort following the order, with smaller number sort first. |
| Group By | Check it if you want the results be grouped by the column. |
| Function | Apply function to the column. |
| Filter | Add filter for the column. |
Supported fitlers
The following table lists out the filters you can enter in the Filter field.
| Filter | Description | Sample |
|---|---|---|
| = | Equals | = 10 |
| <> | Does not equal | <> 250 |
| < | Less than | < 80 |
| <= | Less than or equal to | <= 200 |
| > | Greater than | > 0 |
| >= | Greater than or equal to | >= 18 |
| LIKE | Search for a pattern | LIKE ‘%PRIORITY%’ |
| IN | To specify multiple possible values | IN (‘Administrator’, ‘Manager’) |
| BETWEEN | Between an inclusive range | BETWEEN 10 AND 20 |
| IS NULL / IS NOT NULL | IS NULL: To select records with null IS NOT NULL: To select records with filled values |
IS NULL / IS NOT NULL |
| NOT | Only when no row is returned from the sub query. | NOT EXISTS (SELECT NAME FROM USERS) |
| EXISTS | Only when at least one row is returned from the sub query. | EXISTS (SELECT NAME FROM USERS) |
| ALL | Compares a scalar value with a single-column set of values. | >= ALL (SELECT STOCK FROM PRODUCTS) |
| ANY | Compares a scalar value with a single-column set of values. | >= ANY (SELECT STOCK FROM PRODUCTS) |