L3 is used to provide further detail of the interoperability requirements associated with the operational capability of interest. The focus is on logical flows that cross the capability boundary. Although the primary purpose of the L3 Viewpoint is to specify information exchanges, the L3 may also list flows of materiel, energy and human resources.
Usage
The intended usage of the L3 includes:
- Definition of interoperability requirements.
Creating a Node Interactions (Node-Based) table
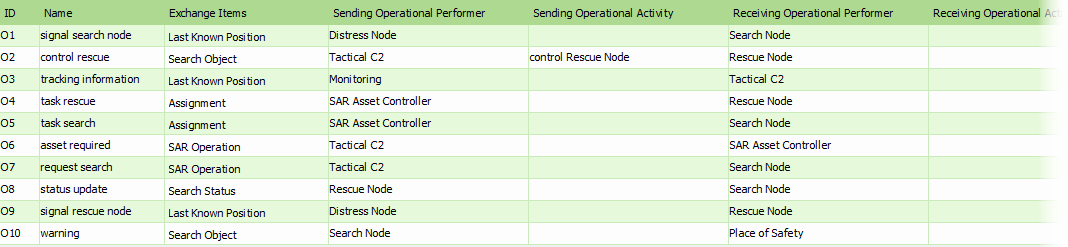
The L3 Node Interactions (Node-Based) table identifies the information transfers that are necessary to enable the nodes to achieve a business objective. It details information exchanges by identifying which nodes exchange what information, with whom, why the information is necessary, and the key attributes of the associated information products.
To create a Node Interactions (Node-Based) table:
- Click on Node Interactions (Node -Based) in the Action Artifact area to open the Node Interactions (Node -Based) table.
- This opens the Node Interactions (Performer-Based) table with OperationalExchanges listed. The OperationalExchanges are defined in L2.
- For each of the OperationalExchanges:
- Select the items involved in operational exchanges.
- Optionally fill in the attributes of operational exchanges.
Creating a Node Interactions (Role-Based) table
The Node Interactions (Role-Based) table specifies the operational flows among nodes. Unlike the performer-based table, the role-based table focuses on the interactions between roles inside the nodes.
To create a Node Interactions (Role-Based) table:
- Click on Node Interactions (Role-Based) in the Action Artifact area to open the Node Interactions (Role-Based) table.
- This opens the Node Interactions (Role-Based) table with OperationalExchanges listed.
- Create a new OperationalExchanges by clicking on the New Operational Exchange above the table.
- This creates a new row of OperationalExchange. Enter its name.
- Select the OperationalConnector that the OperationalExchange realizes. The OperationalConnectors are defined in L2.
- Select the items involved in the operational exchange.
- Optionally fill in the attributes of operational exchange.